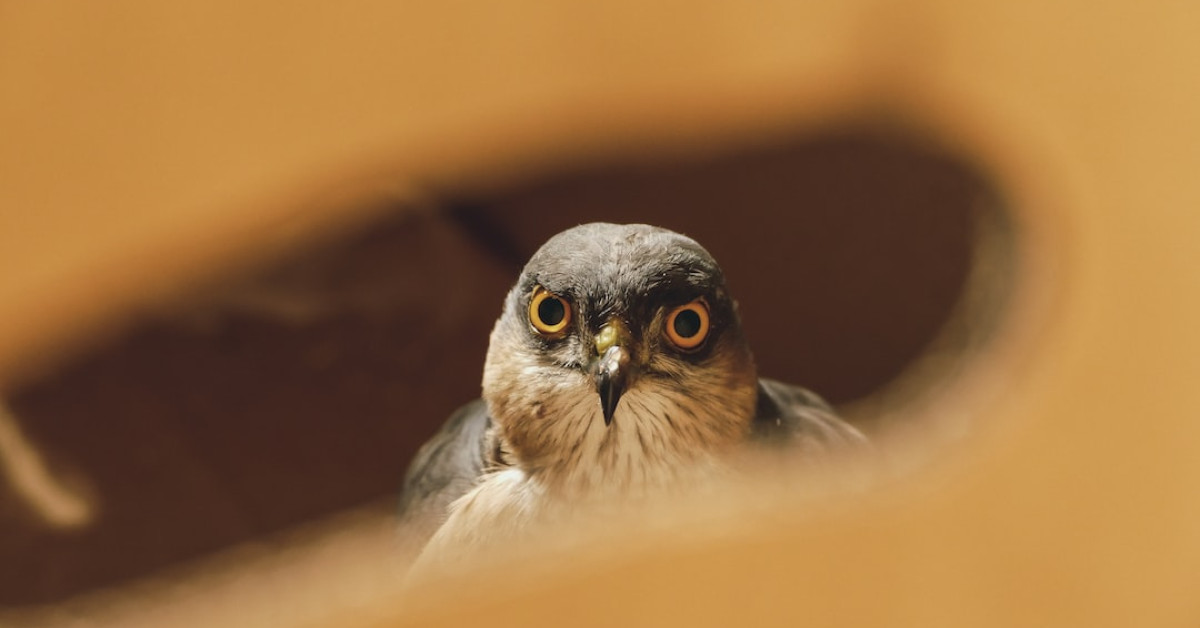
The skies hold a majestic display of aerial prowess as hawks navigate the vast canvas above us. To the avid birdwatcher or the curious onlooker, understanding the nuanced differences between these predatory birds is both art and science. Hawk identification is a skill that transforms a casual glance into the sky into a narrative of survival and grace. As we delve into the world of raptors, our guide will empower you to spot, identify, and appreciate the different species of hawks with unparalleled ease.
The Fundamentals of Hawk Identification
Hawk identification can be an exhilarating challenge, one that requires an eye for detail and a knowledge of the traits that distinguish each species. The first step in becoming a seasoned hawk spotter is familiarizing yourself with the basics.
Anatomy of a Hawk
To accurately identify hawks, one must understand the key anatomical features that define these birds of prey:
- Beak: A tell-tale feature, a hawk’s beak is hooked and designed for tearing flesh.
- Eyes: Hawks have sharp and forward-facing eyes, enabling excellent depth perception.
- Talons: The sharp, curved talons of a hawk are its primary tool for capturing prey.
- Size and Shape: Hawks vary in size, and their body and wing shapes are often indicative of their species and hunting style.
Understanding Molting and Variations
Hawks undergo molting, a process where they shed old feathers for new growth, which can affect their appearance:
- Juvenile vs Adult: Juveniles often have different plumage compared to adults, making age a critical factor in identification.
- Seasonal Changes: The color and pattern of feathers can change with the seasons, adding a layer of complexity to hawk spotting.
Behavioral Cues for Identification
Behavioral observations can also assist in identification:
- Flight Patterns: Hawks display distinctive flight behaviors such as soaring, gliding, or flapping, which can be clues to their species.
- Hunting Tactics: Each species employs unique hunting methods that can help in identifying them from afar.
The Avid Birder’s Toolkit for Hawk Spotting
Preparing yourself with the right tools and knowledge is essential for effective hawk identification.
Essential Gear
To optimize your birdwatching experience, consider the following essentials:
- Binoculars: A pair of high-quality binoculars bring distant hawks into clear view.
- Field Guide: An updated hawk identification guidebook can provide visual references and species information.
- Notebook or App: Record sightings and notes using either traditional or digital means to track your observations.
Learning the Language of Hawks
Comprehending the various calls and sounds that hawks make can provide additional identification markers, from the piercing cries of a Red-tailed Hawk to the softer keening of a Cooper’s Hawk.
Geographic Range and Habitat Preferences
Different species of hawks can be found across various environments. By understanding the geographic range and preferred habitats of each species, you can predict where certain hawks may be found.
Mapping the Skies: Recognizing Raptor Ranges
- Red-tailed Hawk: Widespread across North America, commonly seen perched along highways and in open fields.
- Cooper’s Hawk: Prefers wooded areas and is frequently spotted in both rural and urban settings.
Habitat-Specific Hawks
Understanding the environment is key. For example, a raptor perched in a marshland is likely a different species than one spotted in a desert landscape.
Iconic Hawk Species and How to Spot Them
As we explore the characteristics of specific species, you’ll become adept at distinguishing these feathered predators on the wing.
The Majestic Red-tailed Hawk
Recognizable by its rusty-red tail and broad wings, the Red-tailed Hawk is one of the most common raptors in North America.
- Distinctive Markings: Look for the rich brown plumage on its back and lighter underside with a streaked belly band.
- Behavioral Traits: Often seen soaring in wide circles or perched prominently as it scans for prey.
The Stealthy Cooper’s Hawk
Cooper’s Hawks are known for their agility and secretive nature.
- Distinguishing Features: A smaller hawk with a rounded tail and a distinctive head that appears larger in proportion to its body.
- Habitat Clues: Keep an eye on bird feeders, as Cooper’s Hawks have adapted to hunting in suburban neighborhoods.
The Broad-winged Hawk: A Migratory Marvel
This compact raptor is famous for its spectacular, long-distance migrations in large groups known as “kettles.”
- Visual Identification: A Broad-winged Hawk can be identified by its broad wings and short tail, with distinct barring on the tail and a warm reddish-brown underbelly.
- Migration Patterns: Look to the skies during migration seasons, particularly in mountainous regions where they catch thermals.
Advanced Hawk Identification Techniques
Transitioning from a novice to an expert in hawk identification involves mastering advanced techniques and subtle cues.
Recognizing Age and Sex Variations
Gender and age can influence the size and coloration of hawks. Male hawks are often smaller than females, and juveniles can display markedly different plumage compared to adults.
Interpreting Flight and Hunting Behavior
- Soaring vs Flapping: Some hawks, like the Red-tailed, soar on thermals, while others, like the Sharp-shinned Hawk, exhibit rapid wingbeats.
- Predatory Dives: Notice how some species, such as the Peregrine Falcon, are renowned for their high-speed stoops on prey.
Protecting Hawks: Understanding Conservation Status
Awareness of the challenges hawks face is paramount for their protection.
Threats to Raptor Populations
- Habitat Loss: The destruction of natural environments poses a significant threat to hawk species.
- Pesticides: Chemicals used in agriculture can accumulate in hawks, leading to poisoned populations.
Participating in Conservation Efforts
Contributing to local bird conservation organizations and participating in citizen science projects are tangible ways to aid in the preservation of hawk species.
Embracing the Hawk Identification Challenge
Identifying hawks is a fulfilling venture that enhances our understanding of these awe-inspiring birds. Through diligent observation, gear preparation, and knowledge accumulation, anyone can become adept at spotting the subtle distinctions among raptor species. As you refine your identification skills, remember that each sighting is an opportunity to contribute to the greater narrative of avian life and conservation. Happy hawk spotting!