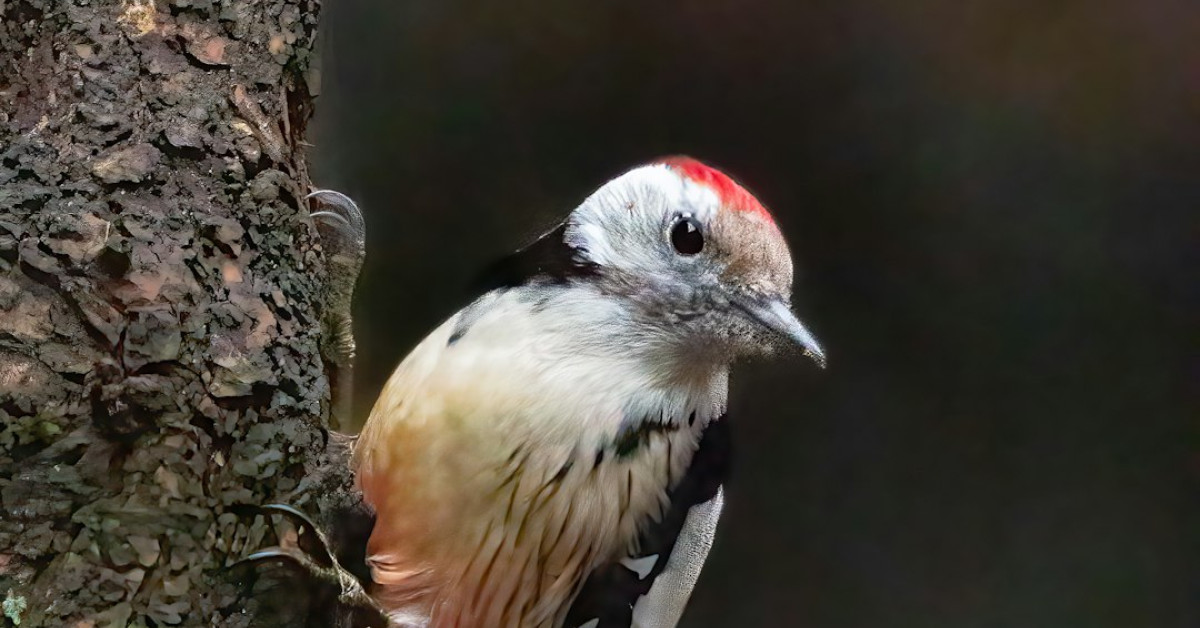
The enchanting melodies of nature often go unnoticed, yet among the orchestra of wildlife, woodpecker species stand as nature’s percussionists, defining the audible landscape of our forests and backyards. As you’re swept into the rhythms of the wild, exploring the many varieties of woodpeckers is a journey into understanding the vitality and ecological significance of these remarkable birds. In this comprehensive guide, you will unearth the secrets of woodpecker behavior, their distinct habitats, and the critical role they play in preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems across the globe.
Woodpeckers are more than just avian creatures; they are symbols of persistence, embodying the spirit of adaptation and survival. Whether you’re an avid birdwatcher, a curious explorer, or someone with a passion for conservation, the intricate world of these birds presents an endless source of fascination. Let’s dive into the robust drumming patterns, vividly-colored plumage, and complex social structures that define various woodpecker species—and understand why these birds are so critical to our natural world.
The Ecological Impact of Woodpeckers on the Environment
Woodpeckers contribute to the environment in ways that are often unseen but fundamentally transformative. Known as “ecosystem engineers,” these birds influence their surroundings profoundly.
- Tree Health and Insect Control: Woodpeckers are natural pest controllers. Their diet primarily consists of insects that can be detrimental to tree health, including beetles and larvae. By feeding on these pests, woodpeckers help to keep forest and urban tree populations healthy.
- Habitat Creation: The cavities woodpeckers carve serve not only as nesting sites for themselves but also as crucial shelters for other species once abandoned. Species such as owls, bats, and even certain mammals benefit from the nesting opportunities created by woodpecker activity.
The Role of Woodpeckers in Forest Dynamics
Forests teem with life due to the ongoing contributions of its inhabitants, including woodpeckers. Their role in forest dynamics is multifaceted:
- Aiding Decomposition: As woodpeckers drill into decaying trees in search of food, they accelerate the decomposition process, contributing to the nutrient cycle within the forest.
- Seeding: Woodpeckers inadvertently become agents of seed dispersal, assisting in the propagation of various tree species.
Anatomy and Adaptation: The Woodpecker’s Toolkit
The anatomy of woodpeckers is particularly specialized, tailored to their unique lifestyle. Understanding their adaptations unveils the evolutionary marvels that enable woodpeckers to thrive in various environments.
Skull and Bill Construction: The Percussionists’ Tools
The skull and bill of a woodpecker are marvels of nature’s design – robust yet exquisitely fine-tuned for their drumming behavior.
- Shock Absorption: Woodpeckers possess a thick skull and specialized muscles that act as a shock absorber during their rapid pecking.
- Chisel-like Bill: Their bills, strong and pointed, are the perfect tools for piercing and chiseling into the bark and wood of trees.
Feet and Claws: Masterful Climbers
Each species of woodpecker is equipped with strong feet and sharp claws, allowing them to effortlessly navigate the vertical world of tree trunks and branches.
- Zygodactyl Feet: Most woodpeckers have two toes facing forward and two backward (zygodactyl feet), providing them the necessary grip to maintain their position while pecking.
A Spectrum of Species: Diverse Woodpecker Enigmas
The world is home to over 200 species of woodpeckers, each exhibiting unique traits and behaviors. From the world-renowned Downy Woodpecker to the enigmatic Ivory-billed Woodpecker, every species is an integral piece of the biodiversity puzzle.
The Downy Woodpecker: A Ubiquitous Presence
Dryobates pubescens, commonly known as the Downy Woodpecker, is among the most widespread and easily recognizable woodpecker species across North America.
- Appearance: The Downy Woodpecker is small, with black-and-white plumage and a distinctive red patch on the head of males.
- Xenia: Its presence in various habitats, from dense forests to suburban areas, makes the Downy Woodpecker a familiar sight for many.
The Pileated Woodpecker: Forest Giant
The Pileated Woodpecker (Dryocopus pileatus) stands as one of the most imposing woodpecker species, known for its size and striking appearance.
- Bold Coloration: This species is adorned with a black body, white stripes, and a prominent red crest that demands attention.
- Cavity Creation: Their ability to create large cavities in trees is unrivaled, making them key players in shaping forest ecology.
The Ivory-Billed Woodpecker: A Ghostly Legend
The Ivory-Billed Woodpecker (Campephilus principalis) is a topic of intrigue and mystery within the birding community.
- Status: Once thought to be extinct, unconfirmed sightings continue to spark hope for its existence.
- Conservation Efforts: Ongoing research and conservation efforts aim to determine the true status of this elusive species.
The Red-Headed Woodpecker: A Striking Vision
Distinct in its appearance, the Red-Headed Woodpecker (Melanerpes erythrocephalus) offers an unforgettable visual contrast in the habitats it occupies.
- Vivid Plumage: With their entirely red heads and black-and-white bodies, they are among the most visually striking woodpeckers.
- Diverse Diet: Unlike many woodpecker species that predominantly feed on insects, this bird has a more eclectic diet, including fruits and nuts.
Habitats and Homes: Where Woodpeckers Thrive
Woodpecker species are spread across a range of habitats from dense woodlands to urban landscapes. Each species has adapted to their specific environment, demonstrating their resilience and versatility.
Forest Dwellers: The Harbingers of Wilderness
In the heart of the forest, woodpeckers find an ideal environment abundant with resources, whether it be food, shelter, or nesting sites.
- Old-Growth Woods: Mature forests provide woodpeckers with a bounty of insect prey and potential nesting sites within aged trees.
- Ecological Role: Within these environments, woodpeckers play a critical role in the health of the woodland ecosystem.
Urban Adapters: Coexistence with Humans
Woodpeckers are not limited to pristine wilderness; some species have carved a niche within urban and suburban areas, adapting to the presence of humans.
- Habitat Adaptability: Despite challenges, such as reduced tree density, these birds demonstrate remarkable adaptability in altered landscapes.
- Human-Woodpecker Interactions: While generally beneficial, interactions can cause conflict, as some woodpeckers may damage wooden structures. However, their presence in cities also aids in controlling pest populations.
Migratory Routes: Seasonal Wanderings of Woodpeckers
Although many woodpecker species are non-migratory, some do undertake seasonal movements to optimize their survival.
- Food Availability: Changes in food resources can prompt certain woodpeckers to relocate temporarily, displaying a level of behavioral flexibility.
- Climate Influence: Weather patterns and temperature shifts can also influence migratory decisions among some woodpecker populations.
Preservation of Habitats: A Conservation Priority
The preservation of diverse habitats is vital for the continued existence of woodpecker species worldwide.
- Protective Legislation: Sustainable forestry practices and protected areas are essential in maintaining the populations of these ecologically important birds.
- Conservation Initiatives: Organizations and individuals alike play a part in habitat conservation, ensuring woodpeckers continue to resonate in nature’s symphony.
Woodpecker Conservation: Safeguarding Nature’s Drummers
The future of woodpecker species is inextricably linked to the health of their ecosystems and our dedication to their conservation. As stewards of the environment, we have the power and responsibility to protect these emblematic birds.
Threats to Woodpecker Populations
Woodpeckers face an array of threats, from habitat destruction to climate change. Understanding these threats is the first step in mitigating their impact.
- Deforestation: Loss of forest habitat, primarily due to logging and land conversion, poses a significant threat to woodpecker populations.
- Environmental Toxins: Pesticides and other toxins not only reduce food availability but also directly affect woodpecker health.
Actionable Steps for Woodpecker Conservation
Active conservation measures can turn the tides for woodpecker species under threat. Here are some ways we can make a difference:
- Supporting Conservation Efforts: Engaging with organizations dedicated to bird conservation can amplify the efforts to protect woodpecker species and their habitats.
- Responsible Land Management: Whether you’re a landowner or a policymaker, responsible land management that considers the needs of local wildlife is crucial.
The Interconnectedness of Bird and Human Life
As avian aficionados or eco-conscious citizens, recognizing our shared world with woodpeckers and other wildlife leads to a greater awareness of our collective impact on the environment.
- Birdwatching Ethical Guidelines: Observing woodpeckers and other birds responsibly ensures minimal disruption to their natural behaviors.
- Educational Outreach: Educating others about the importance of woodpeckers fosters a broader understanding and appreciation of these birds, encouraging protective actions.
Cultural Significance: Woodpeckers in Human Lore
Beyond their ecological role, woodpeckers have also nestled into the cultural narratives of many societies, symbolizing aspects such as determination and the cycles of nature.
- Mythology and Folklore: Various cultures have revered woodpeckers, incorporating them into myths and stories passed through generations.
- Artistic Inspiration: The striking appearance and unique behaviors of woodpeckers have inspired artists and creators, adding to their cultural footprint.
Conclusion: Embracing the Rhythms of Our Feathered Neighbors
Woodpeckers are more than just woodland musicians; they are critical components in the web of life that sustains forests and, by extension, our planet. As we learn about these fascinating birds, their behavior, and their significance, we gain more than just knowledge. We gain a perspective that compels us to act, to conserve, and to coexist with the natural world.
By understanding the different habitats woodpeckers inhabit, the roles they play in environmental health, and the challenges they face, we can become better custodians of our shared home. Whether you look up to the tallest trees in your local park or travel to witness the majesty of woodpeckers in distant forests, remember that each drumming pattern you hear is a call to appreciate and protect these rhythmic guardians of the ecosystem.
Unlocking the rhythms of nature through the study of woodpecker species not only enriches our lives but also reminds us of the deep interconnectedness between all living creatures. In the grand symphony of life, may we strive to ensure that the woodpecker’s beat goes on, vibrant and unwavering, for generations to come.